Nestled amidst the breathtaking Himalayan range, the Kingdom of Bhutan is an intriguing mix of tradition, culture, and modernity.
Bhutan is a gem, from its traditional monasteries to its serene landscapes. However, what truly makes Bhutan distinctive is its language and linguistic diversity. Let’s delve deeper into the official language, Dzongkha, and its significance in Bhutanese culture.
Table of Contents
- Bhutanese Language And The Country Of Bhutan: A Mysterious Gem Amidst The Himalayas
- The Significance Of Dzongkha- Language Of Bhutan
- 15 Fascinating Facts About Dzongkha – The Language Of Bhutan
- Origin In The Fortresses:
- Regional Dominance:
- Roots In Indian Script:
- Sibling Of Sikkimese:
- Medium Of Education:
- Codification Journey:
- Linguistic Elements:
- Spoken Vs. Written Divergence:
- Vocabulary Evolution:
- Nurturing The Language:
- UNESCO Recognition:
- Literary Flourish:
- Influence Of Buddhism:
- Radio And Television:
- Festivals And Celebrations:
- 12 Intriguing Facts About The Mysterious Country Of Bhutan
- Related Questions
Bhutanese Language And The Country Of Bhutan: A Mysterious Gem Amidst The Himalayas
For many, Bhutan remains an enigma. Nestled amidst the breathtaking Himalayan mountains, this little-known kingdom piques curiosity with tales of its pristine landscapes, ancient monasteries, and vibrant festivals.

Yet, beyond these stories, most have yet to tread its terrains or immerse themselves in its rich traditions. This air of mystery surrounding Bhutan only deepens when one delves into its linguistic tapestry, which is as varied and colorful as the nation itself.
At the heart of Bhutan’s cultural identity is its official language, Dzongkha. Beyond merely being a medium of communication, Dzongkha bridges Bhutan’s glorious past to its evolving present.
While the scenic landscapes and traditional monasteries paint a vivid picture, understanding the intricacies of Dzongkha and the linguistic diversity of Bhutan provides a richer understanding of the nation’s soul.
Bhutan, often revered as a gem amidst the vastness of the Himalayas, stands out not only for its awe-inspiring geography but also for the harmony between its age-old traditions and modern aspirations.
It’s a place where the echoes of ancient chants from monasteries seamlessly blend with contemporary discourses. The Bhutanese language is central to this blend, reflecting the nation’s unique essence and telling tales of its majestic heritage.
So, while Bhutan may remain a dream destination for many, encapsulated in layers of wonder and mystique, diving into its linguistic depths can offer a first-hand experience of its cultural richness.
Even without setting foot on its soil, understanding Dzongkha can be a journey into the heart of Bhutan, unveiling stories, traditions, and a way of life that remains beautifully preserved in this Himalayan kingdom.
The Significance Of Dzongkha- Language Of Bhutan
The most crucial language in Bhutan is Dzongkha, but besides Dzongkha, many other languages are also spoken in Bhutan. Read on as we explore more.
Dzongkha, The Language Of The Fortresses:
Derived from the words ‘Dzong,’ meaning ‘fortresses,’ and ‘Kha,’ meaning ‘language,’ Dzongkha aptly captures the essence of Bhutan. It’s not just a medium of communication but a bridge to the nation’s rich heritage and tradition.
As the official language, Dzongkha is prominent in administrative and official matters.
Linguistic Diversity Of Bhutan:
Besides Dzongkha, several other languages are spoken across Bhutan. This diversity reflects the vibrant tapestry of cultures and traditions.
Notable among these are Tshangla, Nepali, Brokkat, and Gongduk. While Tshangla, the mother tongue of the Sharchops, is spoken in eastern Bhutan, Nepali, an Indo-Aryan language, has its speakers in the south.
The languages of Brokkat and Gongduk, though spoken by fewer people, are a testament to the rich linguistic heritage of the country.
15 Fascinating Facts About Dzongkha – The Language Of Bhutan
Dzongkha is not just the primary language of Bhutan, but it is a language that is filled with many fascinating facts. Read on as we explore 15 of the most essential facts of Dzongkha, the language of Bhutan.
Origin In The Fortresses:
As mentioned, Dzongkha translates to the “language of the fortresses.” This emphasizes its connection with the Dzongs, or fortresses, around which administrative and monastic life revolves in Bhutan.
Regional Dominance:
Dzongkha is the native tongue of eight western districts of Bhutan, marking its prominence in the region.
Roots In Indian Script:
Sambhota, the founder of Dzongkha, introduced the Devangiri script, which has its roots in the Indian script.
Sibling Of Sikkimese:
The language resembles Sikkimese, spoken in the neighboring Indian state of Sikkim.
Medium Of Education:
Alongside English, Dzongkha is used as a medium of instruction in Bhutanese schools, promoting bilingualism.
Codification Journey:
Dzongkha stands out as one of the languages codified around fifty years ago.
Linguistic Elements:
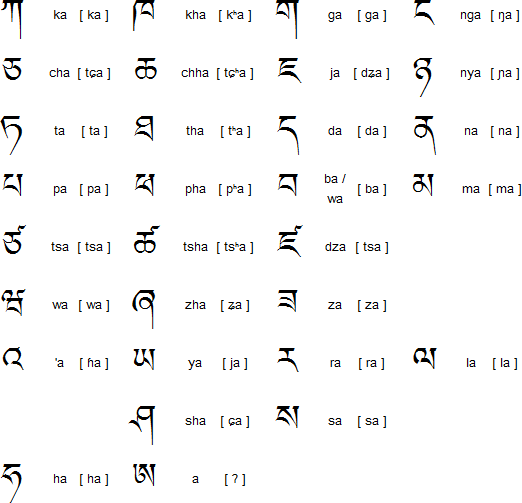
The language boasts thirty consonants, Selje Sumchu, and four distinct vowels.
Spoken Vs. Written Divergence:
An exciting facet of Dzongkha is the stark difference between its spoken and written forms.
Vocabulary Evolution:
With a limited initial vocabulary, Dzongkha sees the constant addition of new words, reflecting the evolving nature of language.
Nurturing The Language:
The Dzongkha Development Commission is dedicated to the language’s growth. The commission is pivotal in Dzongkha’s modern evolution, from preparing glossaries to developing computer fonts.
UNESCO Recognition:
Dzongkha is recognized by UNESCO, emphasizing its importance on the global stage.
Literary Flourish:
Both ancient and modern Bhutanese literature has flourished in Dzongkha, with several works being translated into other languages.
Influence Of Buddhism:
Buddhism profoundly influences Dzongkha and many religious scriptures are written in it.
Radio And Television:
Bhutan Broadcasting Service broadcasts programs in Dzongkha, ensuring its reach and preservation.
Festivals And Celebrations:
Dzongkha plays a central role in Bhutan’s festivals, prayers, and celebrations, echoing its cultural significance.
Dzongkha, the heart and soul of Bhutan, offers a glimpse into the nation’s cultural depth and rich history. Its myriad nuances and fascinating facts make it more than just a language; it’s a testament to Bhutan’s legacy and its stride into modernity.
Whether you’re a linguist, a traveler, or simply someone curious about the world, understanding Dzongkha offers a unique window into the soul of Bhutan.
12 Intriguing Facts About The Mysterious Country Of Bhutan
Bhutan has long remained an enigmatic nation, often considered one of the world’s least visited destinations. Nestled within the Himalayan mountains, it’s genuinely a breathtaking locale.

Land Of The Thunder Dragon:
Bhutan is often called ‘Druk Yul’ in Dzongkha, which translates to ‘Land of the Thunder Dragon.’ This stems from the powerful storms that frequently roll in from the Himalayas.
Gross National Happiness:
Unlike most countries that measure success through Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Bhutan follows the unique Gross National Happiness (GNH) concept. It emphasizes its citizens’ spiritual, physical, social, and environmental health over material wealth.
Carbon Negative:
Bhutan is the world’s only carbon-negative country. This means it absorbs more carbon dioxide than it produces. With its lush forests covering over 70% of the land, the country acts as a significant carbon sink.
Mandatory National Dress:
Bhutanese citizens are required to wear the national dress in public places. For men, it’s the ‘gho,’ a knee-length robe tied at the waist, while women wear the ‘kira,’ a long dress paired with a jacket known as ‘togo.’

No Traffic Lights:
Thimphu, the capital of Bhutan, does not have any traffic lights. Instead, traffic police manage vehicular flow using hand signals.
Protected Tobacco Sales:
Bhutan is the first country in the world to completely ban the sale and production of tobacco, highlighting its commitment to public health.
Only Monarchy:
Bhutan transitioned from an absolute monarchy to a constitutional monarchy in 2008, and it’s one of the last remaining monarchies in Asia.
Unique Festivals:
The country is renowned for its vibrant festivals like Paro Tsechu and Thimphu Tsechu. These events feature elaborate mask dances traditional music, and offer insights into Bhutan’s rich cultural heritage.
Archery Is a National Sport:
Archery isn’t just a sport in Bhutan; it’s an integral part of the nation’s cultural fabric. Competitions, often accompanied by dance and music, are frequent and lively community events.
Himalayan Setting:
Bhutan is home to Gangkhar Puensum, which, at 24,840 feet, is considered the world’s highest unclimbed mountain.
Protected Biodiversity:
The government mandates that at least 60% of the country remain forested. This policy ensures the protection of a diverse array of flora and fauna, making Bhutan a biodiversity hotspot.
Isolated Yet Modern:
While Bhutan opened its doors to tourism only in 1974 and remains selective about tourist inflows, it’s a country that harmoniously blends tradition with modernity, as evident in its education system, urban centers, and infrastructure.
Bhutan remains an enigma for many. Its commitment to maintaining its rich cultural heritage while embracing change, its pristine landscapes, and the unique philosophy of Gross National Happiness make it a genuinely mysterious and mesmerizing Himalayan kingdom.
At A Bus On A Dusty Road, we talk about everything about travel, life, and ex-pat living. We are all about “Living Life As A Global Citizen.” We explore social, cultural, and economic issues and travel.
We would love to have you be part of our community. Sign up for our newsletter to keep up-to-date by clicking here. If you have any questions, you can contact me, Anita, by clicking here.
Listen to our Podcast called Dusty Roads. You can find it on all major podcast platforms. Try out listening to one of our podcasts by clicking here.
Subscribe to our A Bus On A Dusty Road YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Related Questions
What Makes Istanbul So Special?
As a transcontinental city, it is simple, unique, and memorable. It is also an ancient city home to the Roman Empire and, in fact, over four to three other empires. For a long time, the Ottoman Empire controlled Istanbul as it was at the center of the arts. It’s simple as a city with a fantastic skyline that offers anyone visiting a lot of great things to do.
You can learn more by reading What Makes Istanbul So Special? by clicking here.
Why Was Constantinople Renamed To Istanbul?
The city of Constantinople was officially renamed Istanbul in the 1930s. Before this time, many people used the name Istanbul, but only part of the city was within the old city walls. Constantinople was named after the Roman Emperor Constantine, credited with bringing Christianity to the Roman Empire.
To learn more, you can read our blog on Why Was Constantinople Renamed To Istanbul? by clicking here.
Is Istanbul In Europe Or Asia?
Istanbul has the famous Bosphorus Strait used as the dividing line between Europe and Asia. The city is divided almost right down the middle between the European and Asia Continents, so Istanbul sits between two continents. Many consider Istanbul a transcontinental city that is straddled on two different continents.
To learn more, you can read our blog on Is Istanbul In Europe Or Asia? by clicking here.

