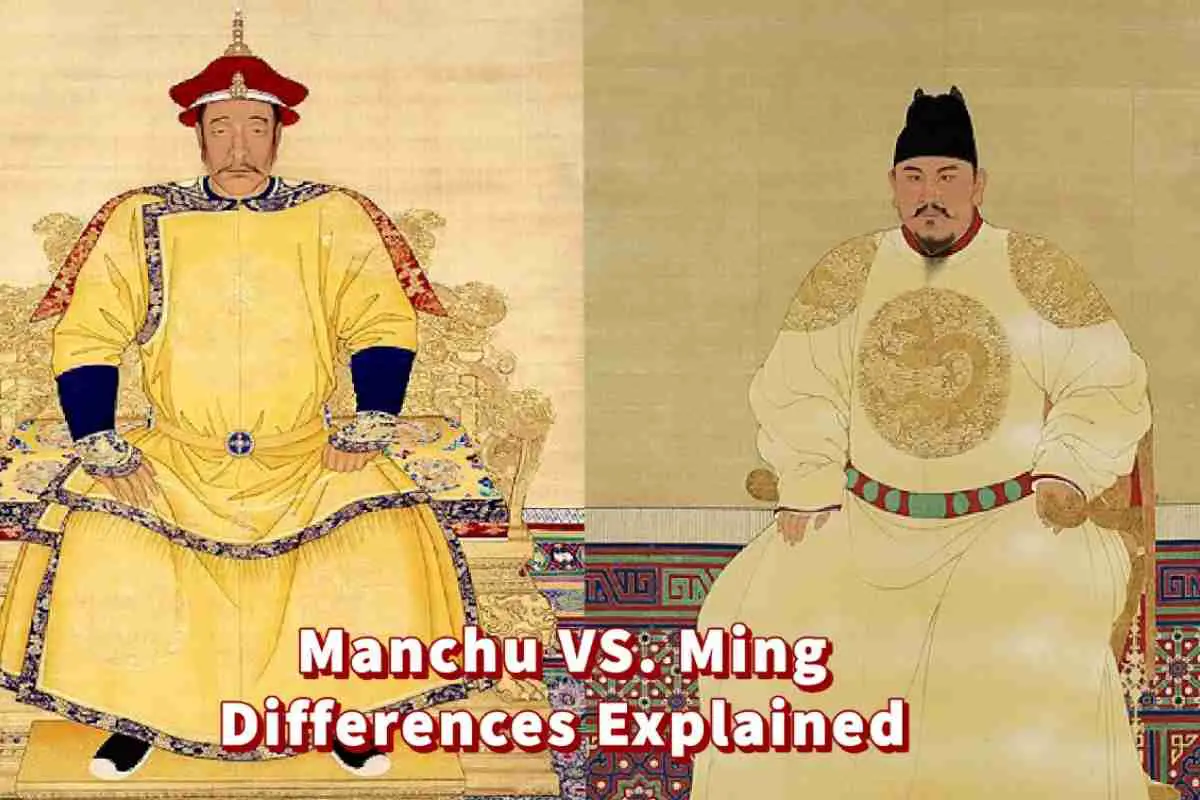
China has a long, rich history, but sometimes confusing history. One of the most confusing aspects is understanding the difference between Ming and Manchu.
The Manchu is a group of people who are also known as Manchurians. They ruled China from 1644 to 1911 and are considered China’s last dynasty. Ming is not a group of people but is a dynasty of China led by Han Chinese. The Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644.
Table of Contents
- Manchu Vs. Ming Explained
- The Ming Dynasty Explained
- The Rise of the Qing Dynasty Or Rise Of The Manchu
- Related Questions
Manchu Vs. Ming Explained
The Manchu is a group living in China, also known as Manchurians. They were the rulers of China under the Qing Dynasty.
Today, China has over 10 million people who consider themselves Manchurian or a Manchu ethnic minority. Many of them have lost their language as they speak mainly Mandarin Chinese.
The Ming is dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644 B.C. It was a dynasty ruled by the Han Chinese, the largest group in China; most Chinese people today identify as Han Chinese.
The Manchu people, also known as Manchurians, gained control of China in 1644 and ruled China under the Qing Dynasty until 1911. The Qing Dynasty was the first Imperial dynasty in China.
The Manchu people came from northeastern China. Throughout China’s history, they considered the Manchu people to be the northern barbarians.
The Ming Dynasty Explained
The Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644. During the time of the Ming Dynasty, China’s population doubled.
The Ming were known for their trade expansion to the outside world and establishment of cultural ties with the West. Many arts flourished during the Ming Dynasty, including drama, literature, and porcelains.
Ming Porcelain became one of the most important exports of the Ming Dynasty. The porcelain was created by grinding china stone, mixing it with china clay, and high-firing it until translucent. Even though porcelain was created during the Tang Dynasty, it was perfected by the Ming Dynasty.
The classic Ming porcelain was blue and white; blue and white porcelain became very popular in Europe.
The Ming Dynasty also helped rebuild much of the Great Wall of China. They believed the Great Wall was one of their best defenses from invasions, particularly from the Mongols north of China.
The Fall of the Ming Dynasty Explained
Near the end of the Ming Dynasty in 1616, Manchurian forces from northeastern Asia defeated the Ming army and occupied several cities on China’s northern border.
Over the next thirty years, wars continued until a full-scale invasion occurred in 1644, and the Manchurian Emperor Shunzhi established the Qing Dynasty of China. The Manchurians, a foreign power, were now ruling China.
This fall of the Ming Dynasty was a significant blow to the Han Chinese, who were and continued to be the majority in China. Han men were forced to cut their hair in Manchu fashion or face execution by the Qing Dynasty.
Other Han intellectuals who criticized the government were rounded up and beheaded. Many Han people were also relocated away from Beijing’s center of power.
The Rise of the Qing Dynasty Or Rise Of The Manchu
The rise of the Qing Dynasty also came with the rise of the Manchu or Manchurians. The Qing Dynasty ruled China for many years (1644 to 1912). Even though they were foreign powers ruling China, they also did things to help China.
Emperor Kangxi ruled for 61 years, from 1654 to 1722; he was the longest-ruling Chinese emperor. Under his tenure, he helped create a Mandarin Chinese dictionary, funded surveys to make maps of China and implemented policies to help farmers.
Potatoes and corn native to the Americas were introduced during Emperor Kangxi’s reign; food was considered plentiful under his reign.
Emperor Kangxi also stopped several military threats and occupied the island of Taiwan. He oversaw exports of cotton, silk, tea, and ceramics.
Under the Qing rulers, China became more conservative. There was an increased demand for purity in women, and men refused to accept any widows as their wives; this led to massive suicide rates of widows unable to support themselves or their children.
In the 19th Century, the Qing Dynasty had many rebellions, such as the Opium Wars and Taiping Rebellions. These conflicts added to the demise of the Qing Dynasty.
You cannot talk about the Qing Dynasty and its demise without mentioning Empress Dowager Cixi; many call her the Dragon Lady. When her husband died, she became the regent for her son and then her three-year-old nephew.
Eventually, she and her nephew fell out; she put him under house arrest. The Empress executed anyone who helped her nephew.
Empress Cixi is credited with helping to ensure the demise of the powerful Manchurian Qing Dynasty. The Qing Dynasty fell in 1911.
End of Manchu Rule in China
The end of the Qing Dynasty in China marked the end of the Manchu rule of China. It was not the end of the Manchu people as many Manchu people lived in China and considered China their home.
With the fall of the Qing Dynasty, many Manchu people assimilated into Chinese culture. They stopped speaking the Manchurian language and instead spoke Mandarin Chinese.
The Manchu language is the language of the Manchurians, who are initially from China and the Korean Peninsula. For a long time, Manchu was the official language of China as it was used during the Qing Dynasty in the royal court and government.
Once the Qing Dynasty fell and many Macburians were chased away from the capital of Beijing to their ancestral homeland in the Changhai mountains, the Manchurian language declined.
Nicole Weers wrote in the Strait Times about the extinction of the Manchu language:
“Today, only 20 people speak this rare language – 10 can be found in Sanjiazi village and the other 10 reside in Dawujia village in China, according to the Unesco’s Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger. Most of the estimated 10 million Manchus living in north-eastern China now speak Mandarin.
Nicole Weers – The Strait Times
The Manchu alphabet, written in vertical columns running from top to bottom and read from left to right, is based on the Mongolian alphabet.”
We can see that even though millions of people in China still consider themselves Manchu or Manchurian, most do not speak their native language. The once-great Manchu people who ruled China have assimilated into Chinese society.
At A Bus On A Dusty Road, we talk about everything about travel, life, and ex-pat living. We are all about “Living Life As A Global Citizen.” We explore social, cultural, and economic issues and travel.
We would love to have you be part of our community. Sign up for our newsletter to keep up-to-date by clicking here. If you have any questions, you can contact me, Anita, by clicking here.
Listen to our Podcast called Dusty Roads. You can find it on all major podcast platforms. Try out listening to one of our podcasts by clicking here.
Subscribe to our A Bus On A Dusty Road YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Related Questions
What Is The Difference Between The Manchu And Han People?
The Manchu people are the people who lived for centuries in what is known as Manchurian or Northeast China. They were the rulers during the Chinese Qing Dynasty. China categorizes the Manchu as an ethnic minority in China. The Han are most people in China, with over 92% of everyone in China Han Chinese.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Is The Difference Between The Manchu And Han People?.
What Happened To The Manchu People In China?
After the collapse of the Qing Dynasty, the Manchu people continued to live in China. The Chinese government categorizes the Manchu people as a Chinese ethnic group. It is estimated that just over 10 million Manchu ethnic minorities live mainly in the Northeastern area of China.
To learn more, you can read our blog on What Happened To The Manchu People In China? by clicking here.