When we think of ancient civilizations, the grand empires of Rome, Egypt, and Greece often come to mind. However, many lesser-known yet equally fascinating ancient empires have significantly shaped the world as we know it today.
These forgotten civilizations contributed to developing language, governance, art, and technology in ways often overlooked by mainstream history books. Read on as we explore some intriguing empires and how they influenced modern nations and cultures. These stories enrich our understanding of history and inspire unique travel ideas for those passionate about discovering the roots of today’s world.
Table of Contents
- 9 Important Ancient Civilizations That Helped Shape Modern Nations
- 1. The Sogdian Empire: The Middlemen of the Silk Road
- 2. The Kingdom of Axum: Africa’s Hidden Power
- 3. The Mitanni Kingdom: The Masters of Chariot Warfare
- 4. The Zapotec Civilization: Architects of Ancient Oaxaca
- 5. The Elamite Empire: The Forgotten Builders of Iran
- 6. The Kingdom of Kush: Egypt’s Rival to the South
- 7. The Nabatean Empire: Masters of Desert Trade
- 8. The Hittite Empire: Pioneers of Diplomacy
- 9. The Khmer Empire: Builders of Angkor
- Related Questions
9 Important Ancient Civilizations That Helped Shape Modern Nations
Here are nine lesser-known but equally captivating ancient empires that have significantly shaped the modern world. These often-forgotten civilizations have left profound legacies in language, governance, art, and technology—contributions often overlooked by mainstream history.
1. The Sogdian Empire: The Middlemen of the Silk Road
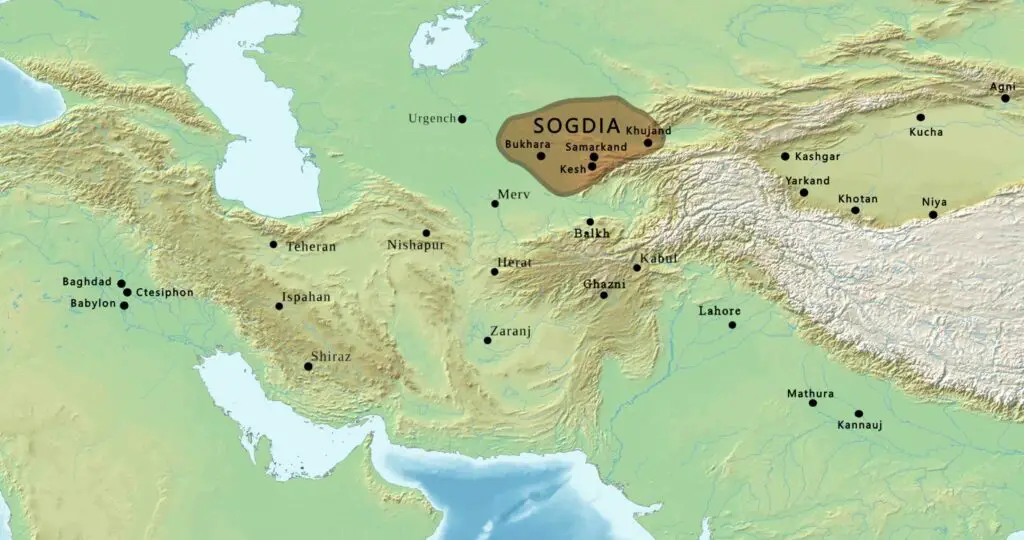
Who Were the Sogdians?
The Sogdian Empire, centered in what is now Uzbekistan and Tajikistan, thrived between the 6th and 11th centuries. While their name may not be as recognizable as the Romans or Persians, the Sogdians were influential as master traders and middlemen along the Silk Road. Their city-states, such as Samarkand and Bukhara, became bustling hubs for commerce, culture, and ideas.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Sogdians contributed significantly to the exchange of art, religion, and knowledge between East and West. They facilitated the spread of Buddhism from India to China and played a crucial role in blending Persian and Chinese artistic styles. The legacy of Sogdian merchants is still evident in modern Central Asian culture, where you can see a fusion of art, textiles, and religious practices that echo their historical influence.
Why Visit?
Travelers interested in ancient trade and cross-cultural interaction should consider visiting Uzbekistan’s Samarkand and Bukhara. Sogdian architecture and culture remain and testify to their influence on the Silk Road.
2. The Kingdom of Axum: Africa’s Hidden Power
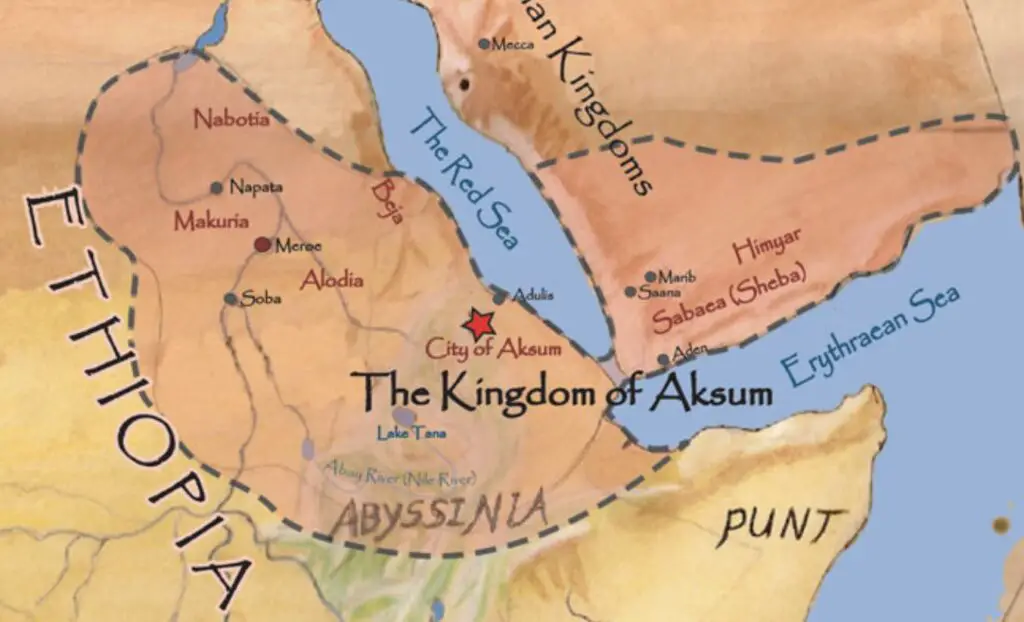
Who Were the Axumites?
The Kingdom of Axum, located in modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, was a powerful trading empire that thrived from around 100 AD to 940 AD. Known for its monumental obelisks and as an early adopter of Christianity, Axum was once considered one of the four great world powers by contemporary Roman and Persian historians.
Influence on Modern Culture
Axum’s adoption of Christianity in the 4th century profoundly affected the region’s religious and cultural identity, laying the foundation for Ethiopia’s Orthodox Christian tradition. Moreover, the Axumites’ architectural advancements, such as their stone-carved churches and grand stelae, continue to be a source of national pride and cultural significance in Ethiopia.
Why Visit?
The city of Axum is a UNESCO World Heritage site. Travelers can see the towering obelisks and the Church of St. Mary of Zion, which many Ethiopians believe houses the Ark of the Covenant. This makes it an ideal historical travel destination for those interested in ancient religious and architectural history.
3. The Mitanni Kingdom: The Masters of Chariot Warfare

Who Were the Mitanni?
The Mitanni Kingdom, which existed from approximately 1500 to 1300 BC, was located in northern Syria and southeastern Turkey. This ancient civilization was known for its military prowess, particularly its mastery of chariot warfare and its influential diplomatic relations with other powerful empires such as Egypt and the Hittites.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Mitanni’s innovations in chariot technology and their equestrian skills had a lasting impact on military tactics in the ancient Near East. Additionally, their pantheon of gods, including elements of Indo-Aryan and Mesopotamian beliefs, influenced religious practices in the region. The Mitanni’s legal and social systems are thought to have had a subtle influence on neighboring cultures, which evolved into aspects seen in modern governance and social structures in the Middle East.
Why Visit?
Although little remains of the Mitanni civilization, archaeological sites in southeastern Turkey and northern Syria provide insights into its complex society. These regions allow travelers to explore lesser-known historical sites once at the heart of ancient innovation.
4. The Zapotec Civilization: Architects of Ancient Oaxaca
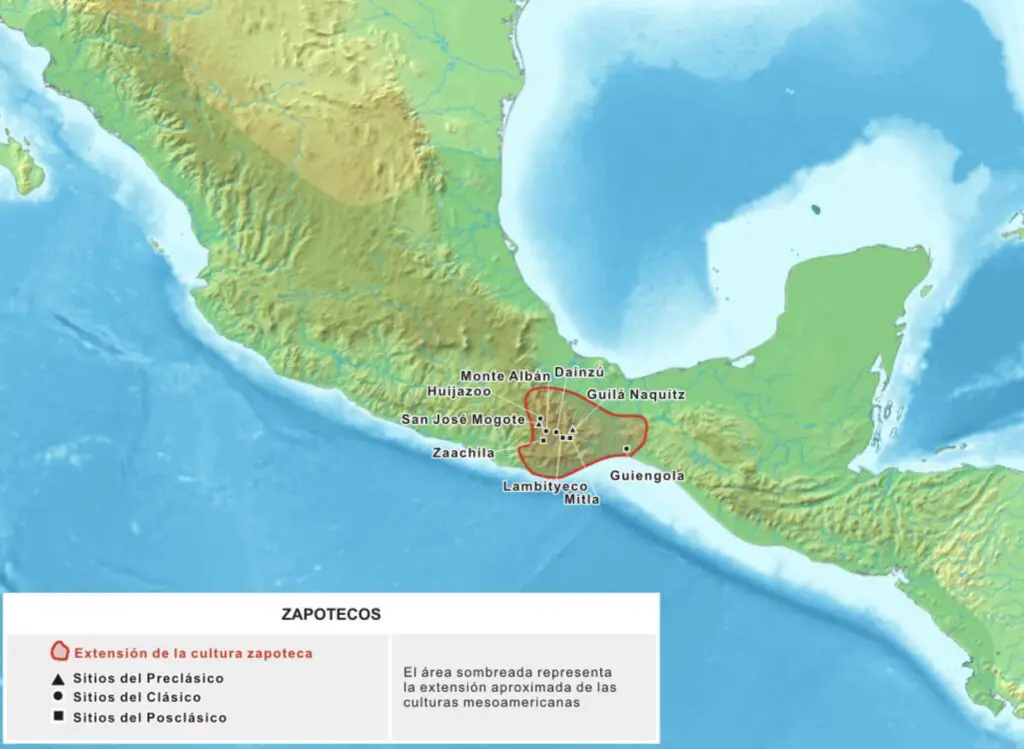
Who Were the Zapotecs?
The Zapotec civilization flourished in the Oaxaca region of Mexico from around 700 BC to 1521 AD. Their capital, Monte Albán, is one of the earliest cities in Mesoamerica and features remarkable examples of early urban planning and monumental architecture.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Zapotecs developed an early writing system and a calendar that influenced subsequent Mesoamerican cultures. Their complex society laid the groundwork for the Mixtec and later Aztec civilizations, contributing to the region’s rich heritage. Today, the Zapotec language and traditions are still alive in many Oaxacan communities, preserving a direct link to their ancient past.
Why Visit?
Monte Albán is a must-visit archaeological site for history enthusiasts. Perched on a hill with breathtaking views of the surrounding valleys, the site offers insights into Zapotec religious practices, art, and governance. The city of Oaxaca, known for its vibrant culture and cuisine, adds another layer to understanding the legacy of the Zapotec people.
5. The Elamite Empire: The Forgotten Builders of Iran
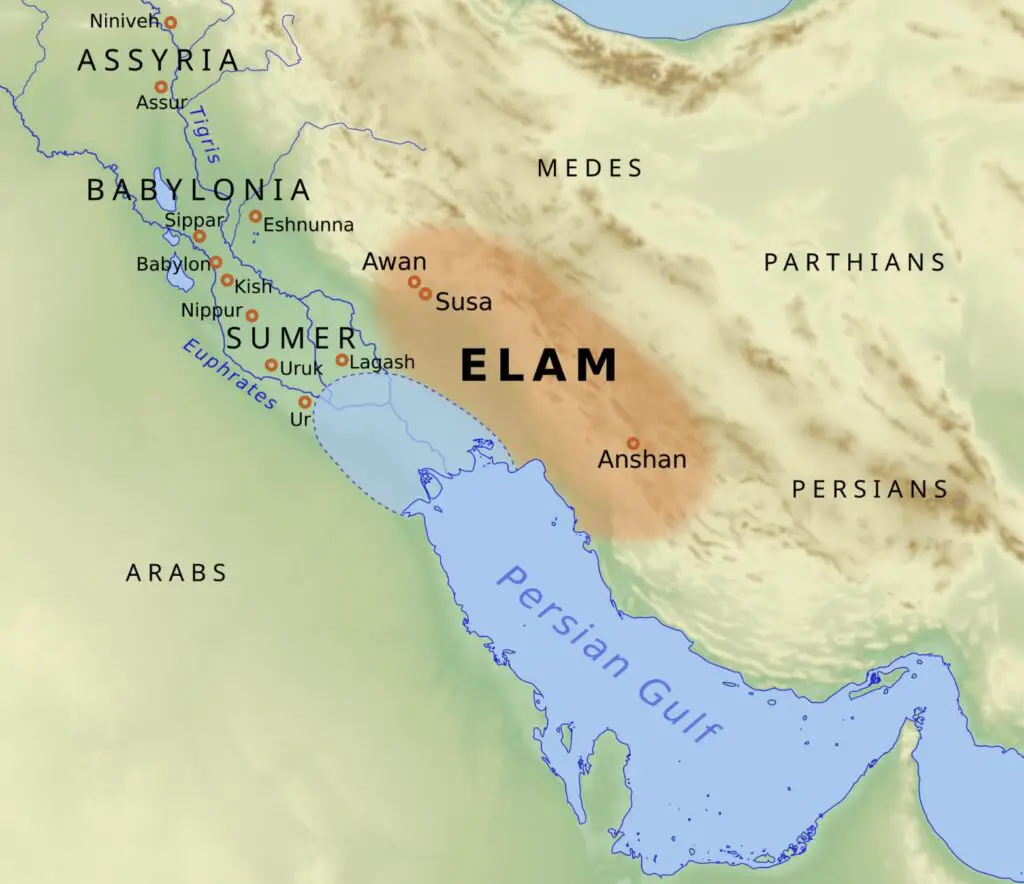
Who Were the Elamites?
The Elamite Empire was an ancient civilization from about 2700 BC to 539 BC in the area corresponding to present-day southwestern Iran. Though often overshadowed by their powerful neighbors, the Mesopotamians and the Elamites significantly contributed to early urban and technological developments.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Elamites were pioneers in art, engineering, and writing. Their cuneiform script, which influenced later Persian writing systems, was essential to the evolution of written communication. The Elamites’ complex societal structures and impressive ziggurats also influenced subsequent Iranian civilizations, contributing to the cultural and architectural heritage seen today in the region.
Why Visit?
Travelers interested in exploring Elamite history can visit the archaeological site of Susa, one of their main cities. This site has historical connections to the Achaemenid Empire and biblical narratives. The nearby Chogha Zanbil ziggurat, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is an impressive testament to their architectural prowess and religious beliefs.
6. The Kingdom of Kush: Egypt’s Rival to the South

Who Were the Kushites?
The Kingdom of Kush, located in what is now Sudan, was a powerful civilization that thrived from around 1070 BC to 350 AD. Known as Egypt’s southern rival and sometimes conqueror, the Kushites ruled as pharaohs during Egypt’s 25th dynasty. Their capital, Meroë, became an important trade, culture, and ironworking center.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Kingdom of Kush is known for its unique pyramids, which are smaller and steeper than those in Egypt. The Kushites also made significant advances in iron smelting, contributing to their economic power. Their legacy is reflected in modern Sudanese cultural and artistic traditions and pride in African heritage and civilization.
Why Visit?
The pyramids of Meroë, part of the UNESCO-listed archaeological sites of the Island of Meroë, are a hidden gem for historical travelers. They are a testament to this often-overlooked empire’s architectural and cultural prowess, offering a glimpse into the ancient grandeur that once rivaled Egypt.
7. The Nabatean Empire: Masters of Desert Trade

Who Were the Nabateans?
The Nabatean Empire was an ancient Arab civilization that flourished between the 4th century BC and 106 AD, primarily in what is now Jordan. Their most famous city, Petra, was a strategic trading hub connecting major trade routes between Asia, Africa, and Europe.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Nabateans are best known for their advanced engineering, particularly their water management systems, which allowed them to thrive in the arid desert. With its rock-carved structures like Al-Khazneh (The Treasury), Petra showcases their architectural innovation and cultural synthesis influenced by Hellenistic, Egyptian, and Mesopotamian styles. The Nabateans’ approach to commerce and their strategic use of resources left a lasting imprint on the region’s trade and economic practices.
Why Visit?
Petra is a must-visit destination for anyone interested in ancient civilizations and breathtaking archaeological wonders. Recognized as one of the New Seven Wonders of the World, Petra offers travelers an awe-inspiring journey into the Nabateans’ engineering brilliance and cultural synthesis.
8. The Hittite Empire: Pioneers of Diplomacy

Who Were the Hittites?
The Hittite Empire was an ancient Anatolian state that emerged around 1600 BC and lasted until approximately 1178 BC. Located in modern-day Turkey, the Hittites were known for their formidable military and as one of the first civilizations to sign written peace treaties.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Hittites advanced in warfare and statecraft, employing chariots and iron weapons, making them a formidable power. Their legacy includes the Treaty of Kadesh, signed with Egypt’s Pharaoh Ramses II, considered the world’s earliest known peace agreement. This emphasis on diplomacy and legal structures influenced future civilizations and set a precedent for conflict resolution and governance.
Why Visit?
The ruins of Hattusa, the ancient Hittite capital, are a UNESCO World Heritage site where travelers can explore remnants of grand temples, royal residences, and fortifications. These ruins provide valuable insight into the sophistication of Hittite architecture and state administration.
9. The Khmer Empire: Builders of Angkor

Who Were the Khmers?
The Khmer Empire, based in modern-day Cambodia, was a powerful Southeast Asian kingdom that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries. The empire is best known for constructing Angkor Wat, the largest religious monument in the world.
Influence on Modern Culture
The Khmer Empire’s architectural and cultural achievements established modern Cambodian identity.
Angkor Wat, originally dedicated to the Hindu god Vishnu, became a Buddhist temple and is a vital symbol of Cambodia’s spiritual and historical legacy. Angkor’s intricate bas-reliefs and sculptures depict scenes from Hindu epics and the Khmer court, offering insights into their cosmology, beliefs, and daily life.
Why Visit?
Angkor Archaeological Park is a UNESCO World Heritage site that attracts history buffs and travelers worldwide. Beyond Angkor Wat, visitors can explore the intricate temples of Bayon and Ta Prohm, immersing themselves in the grandeur and mystery of the Khmer civilization.
While some civilizations, like Rome and Egypt, dominate our historical consciousness, these lesser-known empires played pivotal roles in shaping the world we live in today. From the masterful traders of the Sogdian Empire to the sophisticated governance of the Hittites, these ancient cultures left behind a unique legacy that continues to influence modern nations.
By exploring their stories and visiting the remnants of their grandeur, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of human history and the interconnectedness of our shared past.
At A Bus On A Dusty Road, we talk about everything about history, travel, life, sailing, and ex-pat living. We are all about “Living Life As A Global Citizen.” We explore social, cultural, and economic issues and travel.
We would love to have you be part of our community. Sign up for our newsletter to keep up-to-date by clicking here. If you have any questions, you can contact me, Anita, by clicking here.
Listen to our Podcast called Dusty Roads. You can find it on all major podcast platforms. Try out listening to one of our podcasts by clicking here.
Subscribe to our A Bus On A Dusty Road YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information.
Related Questions
Are Hmong People And Mongol People Related?
The Hmong people are from China and have migrated to southeast Asia, mainly Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and Myanmar (Burma). The Mongols, also known as Mongolians, live primarily in Inner Mongolia (China) and Mongolia. The Hmong mainly live in the mountains, whereas the Mongols are nomadic herders.
By clicking here, you can discover Are Hmong People And Mongol People Related?
What Happened To The Hmong After The Vietnam War?
When the Vietnam War ended, the Hmong in Laos was in a terrible position; the Hmong fighters were enemies of the present Laotian government and considered “persona non gratis.” Some were forced into labor camps or kicked out of their home and lands. The Hmong eventually made their way to the Laotian – Thai border to try to get into the United States via Thailand.
By clicking here, you can discover What Happened To The Hmong After The Vietnam War?
Are Miao And Hmong The Same People?
Miao is a Chinese term used for the ethnic hill tribes that are Hmong, Hmu, Qo Xiong, and A-Hmao people. If someone says they are Miao, you can not automatically assume they are Hmong as they could be one of these four ethnic classified groups.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Are Miao And Hmong, The Same People?

